Kip Hansen's news briefing – February 8, 2025 – 1000 words
A new study by the University of Florida and the University of Colorado School of Mining, by Emma J.
“47 Years of Great Antarctic Calving Incident: Insights from Extreme Theory”
Note (Abstract):
“We used iceberg sizes for 47 years from satellite observations. Our analysis shows that during this time frame, the largest iceberg iceberg surface area of the year has no upward trend. This finding suggests such as the recent 2017 Larsen C Iceberg The extreme calving events are statistically statistical, and extreme calving events are not necessarily the result of climate change.”
The conclusion is more accurate:
“…Our analysis shows that the maximum calving size did not increase during our study intervals. Instead, very large calving events are likely to be typical of healthy ice cap systems where a quasi-stable calving size exists Cycles of advancement and retreat. The lack of upward trend in the largest iceberg area of the year may be attributed to the overall increase in the number of smaller calving events, which may have inhibited the development of extremely large calving events.”
As with all the results of these types of studies, the authors must be read carefully.
1. Over the past 47 years (the range of reliable data), “The maximum calving size has not been increased yet”.
2. ”Very large calving events may be typical of a healthy ice cap system where there is a quasi-stable cycle of calving advancement and retreat. ”
3. There is one “…The largest iceberg area of the year lacks an upward trend.”
4. Then follow a series of “posses” and “possesses” that avoid surfaces: “It may be attributed to the overall increase in the number of smaller calving events, which may have inhibited the development of extremely large calving events.”
Basically, it has been proven that the villain’s climate change will not lead to a large increase in icebergs, allowing it to be stored on ice shelves in Antarctica.
Instead, from their research, large iceberg ruptures are part of the completely normal and expected behavior of these ice shelves.
This is a serious study based on a large amount of computing power and has adopted some novel approaches.Get to know their [sea ice and massive icebergs] Body drivers, time trends and future possibilities”Includes Extreme Value Theory (EVT).
The author tries to mitigate unexpected discoveries by assumptions rather than larger icebergs, but with many smaller icebergs: “Although extreme calving events did not grow in the region during the observation period, overall ice shelf area is decreasing (Greene et al., 2022). Our results show that this mass reduction is driven primarily by small calving events. ”
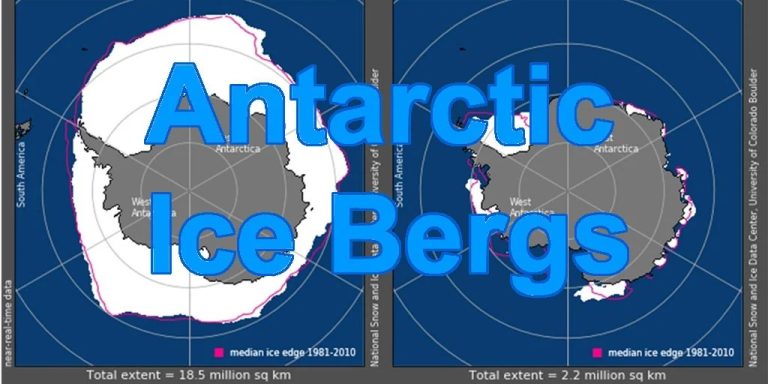
Let's check it outThe overall ice shelf area is decreasing” (This should mean during the 47-year study period): (These two figures cover the years with the study 1979-2024/5, while the study uses 1976-2023)

The above is the Antarctic sea ice range, millions of square kilometers, at the peak of Antarctic summer, with 2025 in the middle of the packing, and the same as the earliest years of the 1980s.

This picture shows the amount of sea ice… Indicates that 2024 is unusually low, but if we emphasize the higher years since 2010, we will get this:

Most of the years in the past 15 years have been higher/highest years. So maybe the author can get a closer look at long-term statistics. The authors cite a study, Greene et al. (2022), support “The overall ice shelf area is decreasing.”
Bottom line:
1. It is incorrect to repetitively say that Antarctica is producing larger and larger icebergs. There is no trend for large numbers of iceberg calving from Antarctic ice shelves (possibly negative).
2. In recent years, the large icebergs that have been suppressed have not been caused by climate change, but are clearly only part of the long-term cycle of ice shelf growth and decline.
3. Pay attention to the Antarctic ice shelf area (km)2) It seems to be overheating… The area covered by ice shelves on the Antarctic coast varies greatly and is currently in line with the scope of the 1980s.
4. The media claims that the opposite is wrong, mainly based on the unreal climate crisis narrative speaking point: “The ice op is melting.”
#####
Author's comments:
Arctic sea ice on the Arctic Ice Sheet is currently in low ice mode, similar to the 1930s. So much so that the Northeastern route from Europe to Asia (North Sea Route) is again commercially transported every year. Russia uses this window to bring its liquefied natural gas from it on seasonal ice Arctic LNG 2 project Go to China and elsewhere.
Antarctic sea ice varies greatly in range and “thickness”. Use satellite to use an image “measure” range that can be compared annually. Currently, thickness is estimated using the satellite’s gravity measurement and the Global Iceberg Modeling and Assimilation System (GIOMAS).
It is well known that melted sea ice does not increase sea levels or cause sea levels to rise. Only melted land ice (glacier ice) can do it.
It is a good thing to have less ice in the North Pole of Earth, as it allows for shorter routes of transport in our more interdependent commercial society. Antarctica's sea ice is a negligible issue. The mass of ice on the Antarctic is a scientific controversy.
Thank you for reading.
#####
Related
Discover more from Watt?
Subscribe to send the latest posts to your email.