
This summer has been marked by frigid outdoor pools eagerly welcoming guests, concrete scorching the soles of bare feet, and popsicles melting in the relentless heat. [emphasis, links added]
In August, the European Commission's Copernicus report found that global average temperatures had hit a record high in the past 12 months, rising 1.51 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Similarly, Roy Spencer and John Christie of the University of Alabama in Huntsville used satellite data to determine that average temperatures in August were 0.88 degrees Celsius warmer than the 30-year average from 1991 to 2020.
“Extreme heat is not only an environmental crisis, it also poses a serious threat to our public health that communities across the country are grappling with,” Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra said in a press release .
“What we are facing today is not what we experienced 30 or 40 years ago. The world we live in is a different world.
On August 14, President Joe Biden released the National Heat Strategy 2024-2030, fulfilling a July promise to take additional action to address rising temperatures. , the increase in temperature is mainly caused by human activities.
“Stabilizing the climate requires drastic, rapid and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and achieving net-zero CO2 emissions.” Zhai Panmao, a Chinese climatologist and co-chair of IPCC Working Group 1, said in a press release.
“Limiting other greenhouse gases and air pollutants, especially methane, may have health and climate benefits.”
Ned Nikolov, a physical scientist and researcher at Colorado State University, told The Epoch Times The IPCC is incorrect about carbon dioxide.
“Greenhouse theory claims that the composition of the atmosphere is important,” Nikolov said. “They believe that small increases in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can cause global warming we have to Stop burning fossil fuels to avoid dangerous climate change.
“That's completely wrong.”
On August 20, Nikolov and retired U.S. Forest Service meteorologist Carl Zeller published their study, finding Recent warming is not the result of increased carbon dioxide.
Instead, after analyzing satellite data, The two researchers concluded that the planet is warming because global cloud cover has decreased, allowing the planet to absorb more sunlight.
Albedo and climate
According to NASA, Earth's atmosphere is constantly trying to balance the planet's “energy budget”—the amount of energy entering and leaving the planet.
After the sun's shortwave radiation (sunlight) reaches the Earth, the energy flows back into space in the form of thermal radiation.
If this balance is disrupted and more sunlight is absorbed or not enough heat escapes to space, Earth's temperature will rise.
The imbalance in the energy budget is called radiative forcing, with incoming radiation being shortwave and outgoing radiation being longwave (or heat).
Additionally, the Earth's albedo (the proportion of sunlight reflected back into space) affects the amount of radiation that reaches the surface.
The IPCC noted in its Sixth Assessment Report that as human greenhouse gas emissions increase concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the Earth's energy budget is imbalanced – more heat energy is trapped, leading to rising temperatures and warming oceans.
It also notes that regarding the Earth's albedo, Between 1950 and 1980, “there is evidence of a general decline (or dimming) of surface solar radiation” Subsequently, “many observation locations have partially recovered (brightened) since then.”
As for why, the IPCC states: “Decades of changes in human factors [human-caused] Aerosol emissions are thought to be a major factor (medium confidence), but multidecadal changes in cloud cover may also play a role.
also, The IPCC stated that some studies have shown that “cloudy days” can have the effect of “darkening” and “brightening”.
However, The contribution of aerosols and clouds to dimming and brightening remains controversial, and “the origins of these trends are not fully understood.”
According to Nikolov, this is where his research comes in.
Challenge the IPCC
“Climate is controlled by the amount of sunlight absorbed by the Earth and the infrared energy emitted into space. These amounts and their differences determine the Earth's radiation budget,” notes the NASA Cloud and Earth Radiant Energy System (CERES) website.
Since March 2000, a US NASA team has been collecting satellite data to examine energy exchange between Earth and space.
Using these measurements and “a novel climate sensitivity model derived from independent NASA planetary data,” Nikolov and Zeller assessed the impact of the Earth's albedo decline on global temperatures in the 21st century.
“CO2 is an invisible trace gas that does not interfere with sunlight. People think it captures thermal radiation from the surface, but this is a misconception because carbon dioxide absorption of long-wave radiation and heat capture are completely different physical processes. According to the second law of thermodynamics, there is no heat absorption in an open system such as the atmosphere.,” Nikolov said.
he added Although water vapor is also a greenhouse gas, it becomes visible when it condenses and forms clouds. And because clouds “reflect solar radiation back into space” Their impact on climate is “measurable and significant.”
“The formation of clouds is controlled in part by cosmic forces. When cloud cover decreases, the planet's albedo decreases and more radiation reaches the surface, causing temperatures to rise.“
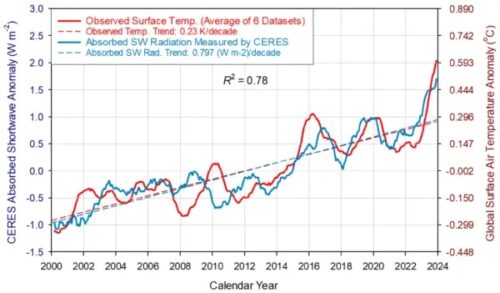
“In our paper, we show how to use [Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System] platform, that is The warming of the past 24 years is entirely due to the observed decrease in Earth's albedo, not to increasing greenhouse gas concentrations, as the IPCC claims.
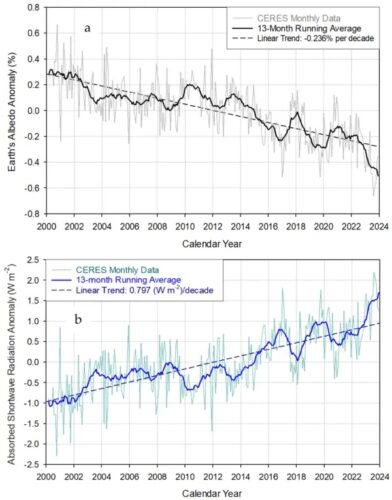


In greenhouse theory, the composition of the atmosphere is “very important” for the planet's global surface temperature, Nikolov said.
By performing a dimensional analysis of NASA data describing the environments of different planets and moons in the solar system, including Earth, Nikolov and Zeller discovered a new universal relationship across planetary bodies.
This shows The atmosphere warms the surface not through longwave radiation from greenhouse gas emissions but through total pressure— Adiabatically, with no loss or gain of heat — and Atmospheric composition does not affect global temperature.
Adiabatic heating (also known as compression heating) is a well-known thermodynamic process. This revolutionary discovery about the physical properties of the atmospheric heating effect, currently known as the greenhouse effect, was published in [our] Peer-reviewed literature in 2017,” Nikolov said.
“That's why when you get higher, whether you're on a mountain or on an airplane, it gets colder because the pressure decreases with altitude.”
He compared the lunar surface temperature measured by NASA with Earth's global temperature to assess the thermal effects of the atmosphere.
“The data shows that the moon is a perfect, airless version of the Earth because it orbits the sun at the same distance as the Earth but has no atmosphere. Therefore, the temperature difference between the Earth and the Moon provides us with the net heating effect of the Earth's atmosphere.“
Nikolov discovered The moon's average temperature is about 88 degrees Kelvin cooler than Earth's. This is important, he said.
“Currently, the greenhouse theory claims that without an atmosphere, the Earth would only be about 33 degrees cooler than it is now. Some estimates even say it would be only 18 degrees cooler.
“so, Current theories severely underestimate the actual thermal effects of the atmosphere. However, this 88 degree thermal enhancement is due to total pressure.
“This is one of the fundamental differences between greenhouse theory and our new climate concept.”
By analyzing the Earth's energy imbalance (EEI), “calculated as the difference between absorbed shortwave radiation and outgoing longwave radiation at the top of the atmosphere,” Nikolov and Zeller discovered that the scientific community had misunderstood it.
“EEI is not caused by ‘heat absorption’ caused by increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, as currently claimed. But “it is caused by the adiabatic dissipation of thermal energy of the ascending air mass in the troposphere due to the decrease in atmospheric pressure with altitude.” ” Nikolov said.
Specifically, Nikolov and Zeller used mathematics to prove EEI is a “superficial phenomenon” rather than a “real imbalance”, This must mean, they say, that the Earth system will not store heat over the long term by increasing greenhouse gases, or “pipeline warming” as the latest IPCC report claims.


Where are the clouds?
Nikolov said the decrease in Earth's cloudiness could have several causes, including galactic cosmic rays, solar wind and interactions between the Sun's and Earth's magnetic fields.
“We have some hypotheses about what's driving changes in cloud cover, but We have no exact mechanism or conclusive theory,” Nikolov said. “That's why we can't yet describe it mathematically in models to make predictions.”
He called for “large-scale interdisciplinary research into the physical mechanisms that control Earth's albedo and cloud physics,” They are “the real drivers of climate on multi-decade timescales.”
“Current climate science acknowledges that cloud cover has been decreasing and the Earth’s albedo has been decreasing, but they attribute this to internal climate change. This is not correct!
“Changes in cloud cover and albedo are externally forced. Identifying such external forcing is the focus of future research, rather than studying carbon emissions and [greenhouse gas] Radiative forcing,” Nikolov said.
If the rise in global temperatures is caused by greenhouse gases, then the extent of warming should be greater than observed, he said.
Rest while reading The Epoch Times
